Set Up Preferences
What are Preferences?
Preferences serve as the foundational optimization settings that dictate the global constraints and parameters within which the optimization algorithm operates to generate an optimal solution. These settings are crucial for defining the boundaries of the problem space, configuring the optimizer to enable efficient and effective outcomes. By establishing clear preferences, users can fine-tune the optimization process to align with specific business objectives and operational limitations. To cater to multiple business scenarios, you can:
-
Save multiple preference configurations to your account. Each configuration can represent distinct use-cases based on variables like vehicle types, routing objectives, operational constraints or more.
-
Load preferred settings before submitting a request to optimize various problems with different preferences.
How to Set Up Preferences in Route Planner?
Route Planner allows for quick and easy selection of parameters to establish your preferences. This section provides a quick demonstration of how to set sample preferences, followed by detailed explanations and context for each available option.
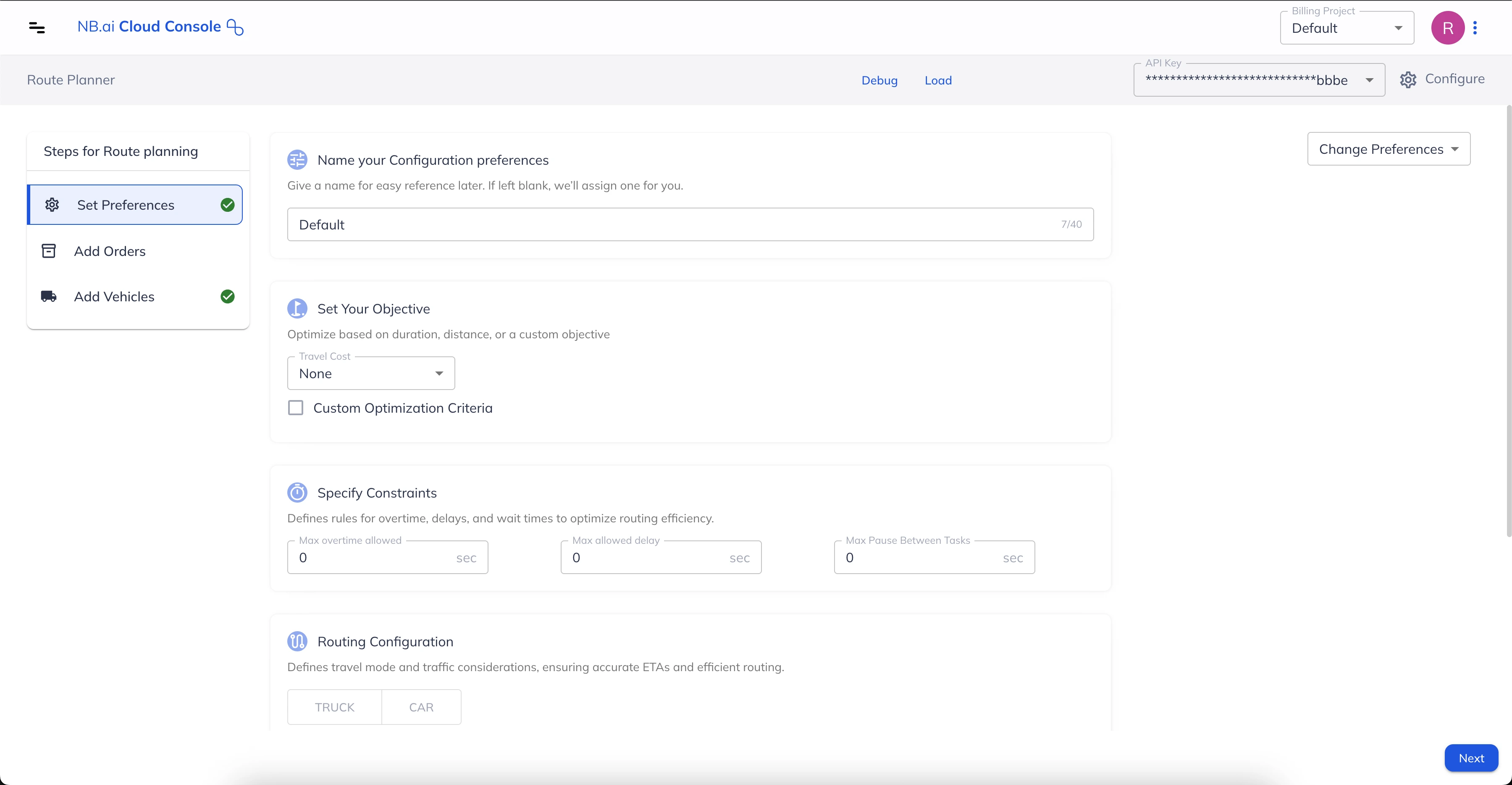
Next, we will cover each preference setting in detail.
Name the Preference Configuration
Start with adding a name for your preference configuration. Next time you log in, your preferences will be automatically loaded. You can also create multiple preference configurations and choose one of them before you start optimizing routes.
Define your Objective
This preference offers different options to tweak the optimization algorithm so that it serves to achieve the required outcome while optimizing the routes. Let’s cover each of them one-by-one:
Travel Cost
This choice determines the metric used to estimate the solution's cost, guiding the optimizer to favor solutions with a lower cost value.
As an example, if Duration is selected, then driving time of all the routes is used to determine the overall cost of the solution and a route with lesser drive time is preferred over other routes, subject to other constraints.
Users can select any one of “Distance”, “Duration” and “Air Distance” options.
Custom Object
In case the business scenario is such that traditional minimization techniques are not good enough, the Route Planner offers customized objectives to solve niche use-cases easily. With custom objectives, users can choose to either minimize or target an even distribution of a given metric. Let’s take a look at the available options:
Type min
When using this value, the algorithm minimizes the metric selected under “Value”. With this type users can choose to minimize either the number of “vehicles” used in the solution or the “completed_time” by which all the feasible tasks are fulfilled.
Type min_max
When using this value, the algorithm aims for equal distribution of the selected “Value”. With this option, users can either go for equally distributing the “tasks” among all the routes or go for having similar “travel_cost” for all routes. The travel cost to be used is identified from the input of the “Travel Cost” field.
Specify Constraints
Constraints relate to the hard and soft constraints that can be used to emulate real-world operating conditions while building the optimization problem. This section allows you to set:
-
Max overtime allowed: The additional time, in seconds, for which a vehicle can operate beyond their shift timings. This is a soft constraint and applies to all vehicles specified in the problem. The optimizer will use the extra shift time only if necessary, as the first preference is to complete all assigned tasks within standard shift timings.
-
Max allowed delay: The additional time, in seconds, beyond a task’s time window during which they can be fulfilled. This is also a soft constraint and applies to all tasks in a given problem. The optimizer will use the extra time only when necessary, as the first preference is to complete all tasks within their original time windows.
-
Max Pause Between Tasks: The maximum time, in seconds, that a vehicle can wait for the task’s time window to begin so that it can be serviced. This is a hard constraint, meaning that if a vehicle needs to wait more than the input value, the optimizer will keep the task unassigned. This constraint applies to all tasks specified in the problem.
Routing Configuration
A set of constraints allowing you to set the following preferences related to routing:
-
Mode: It is used to select the driving mode or the type of vehicles used in the optimization problem. You can choose either “TRUCK” or “CAR”. If not specified, the default driving mode is “CAR”.
-
Traffic Timestamp: Specify a departure time which is used to determine realistic ETAs and smart routes based on the typical traffic conditions at the given time.
Time Zone
Select your Time Zone. All arrival, delivery and completion times in the solution will be affected by this setting.
Send Route To
This preference allows you to select a “connection” to which the routes should be dispatched after they are optimized.
A connection is an authorized integration with third-party fleet management and telematics providers. To add a connection in the NB.ai Cloud Console, go to Fleet Hub > Integrations and select “Add New Connection”. Please reach out to support@nextbillion.ai in case of any issues with adding new connections.
Once the preferences are set up, go ahead with configuring the optimization problem using the Add Jobs, Add Shipments or Add Vehicles step as required.