Draw a route line with the alternative route on NavigationMapView
Draw multiple route lines on NavigationMapView, with one of them designated as an alternative route.
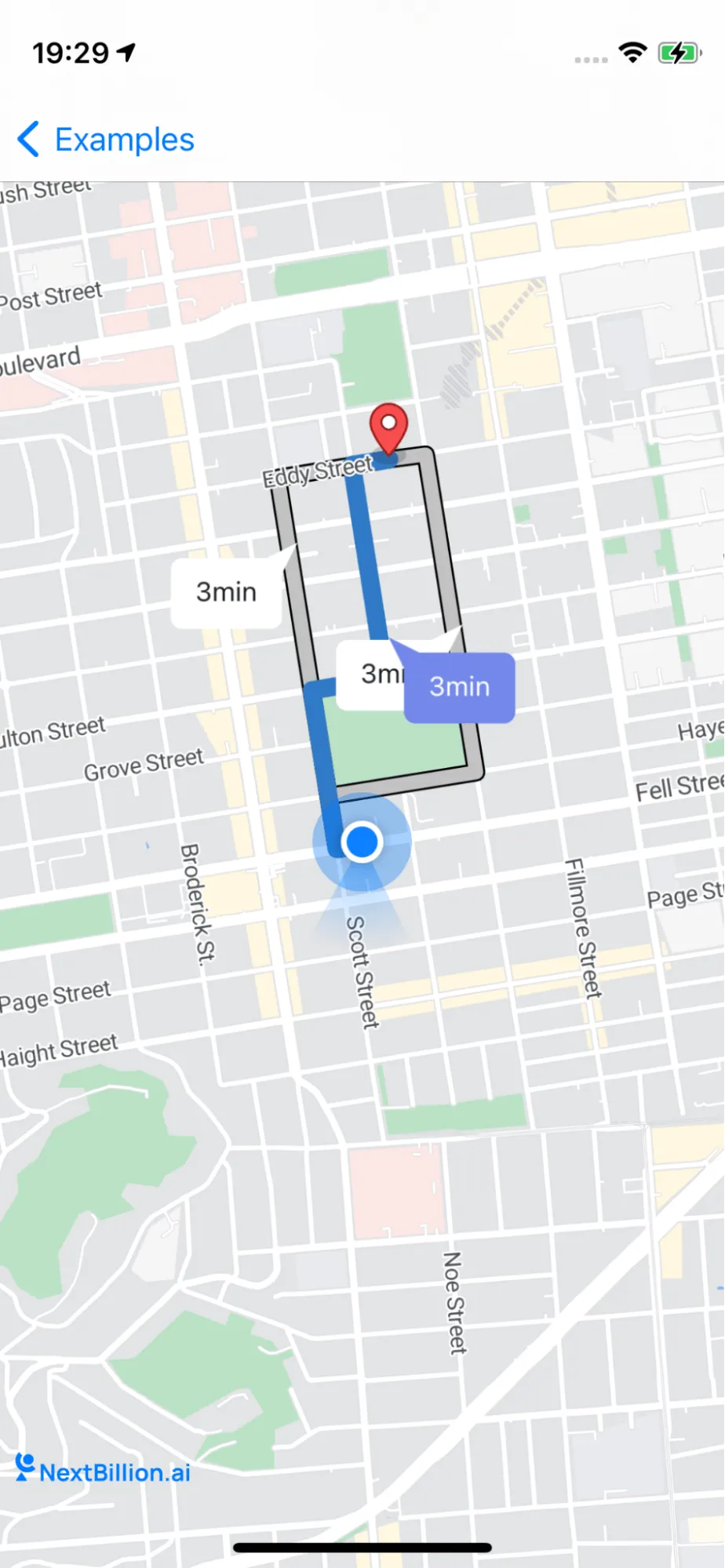
This example shows how to draw multiple route lines with one selected as an alternative route on NavigationMapView
-
We first request a route with NavigationRouteOptions and enable includesAlternativeRoutes as true, this allows the backend to calculate and provide multiple route lines
-
Then we can set one of the routes as an alternative route and show all the route info on NavigationMapView
For all code examples, refer to Navigation Code Examples
DrawAlternativeRouteController view source
The code first creates a NavigationRouteOptions object. This object specifies the parameters for the route calculation. In this case, the options specify that the route should include an alternate route, that it should avoid toll roads, ferries, and highways, and that it should be calculated in imperial units. The code then calls the calculate() method on the Directions object. This method calculates the routes and returns them in an array. The code then loops through the array and displays the routes on the map. The code also defines a delegate method called navigationMapView(_:didSelect:). This method is called when the user selects a route. The method removes the selected route from the array and inserts it at the beginning of the array. This ensures that the selected route is always displayed at the top of the map. Here is a more detailed explanation of each step in the code:
-
Create a NavigationRouteOptions object.
This code creates a NavigationRouteOptions object. The origin property specifies the starting location of the route, and the destination property specifies the ending location of the route.
-
Set the options for the route calculation.
This code sets the options for the route calculation. The includesAlternativeRoutes property specifies that the route calculation should include an alternate route. The roadClassesToAvoid property specifies that the route should avoid toll roads, ferries, and highways. The distanceMeasurementSystem property specifies that the distance should be measured in imperial units. The profileIdentifier property specifies that the route should be calculated for a car. The departureTime property specifies the time at which the route should start. The locale property specifies the locale in which the route instructions should be written. The mapOption property specifies that the route should be calculated using Valhalla. The shapeFormat property specifies that the route should be returned as a polyline.
-
Calculate the routes.
This code calls the calculate() method on the Directions object. The calculate() method calculates the routes and returns them in an array. The code then checks to make sure that the calculation was successful. If the calculation was successful, the code stores the routes in a variable.
-
Display the routes on the map.
This code displays the routes on the map. The showRoutes() method displays the routes as lines on the map. The showRouteDurationSymbol() method displays a symbol on the map that shows the duration of each route. The showWaypoints() method displays the waypoints for each route on the map.
-
Define a delegate method to handle route selection.
This code defines a delegate method called navigationMapView(_:didSelect:)