Snap To Roads API
Introduction
NextBillion.ai’s Snap To Roads API takes a series of locations and snaps them to nearby roads representing the best-matched route where a trip took place connecting all the given locations. Users can choose to retrieve a geometry of the route connecting all the points while using several other configurations. They can also choose to receive the segment-wise speed limits of the route identified in the response.
GET Request
Users can build a basic GET request using the 2 required parameters, key and path, to obtain accurate road-snap data. They can further customize the request by including other optional parameters as listed in the table below.
It is recommended to use the GET method when the number of coordinate points in the path parameter is less than 100.
Request Parameters
Loading..POST Request
Snap To Road API supports HTTPS POST method as well. The parameters and their properties for the POST method are the same as listed in the Request Parameters section. The key is passed as a query parameter whereas other parameters need to be part of the Request Body. An example of a POST request is added in the Sample Queries section below.
Please note that the maximum number of path coordinate points allowed in a POST request is 200.
Response Schema
Loading..Sample Queries
GET Request Example 1
Let’s create a simple snapToRoad request with:
-
4
pathcoordinate points that need to be snapped to the nearest road -
radiusesvalues configured for each of thepathcoordinate points -
timestampsadded for each of thepathcoordinate points
Request
Response
Here is a visual representation of the above response
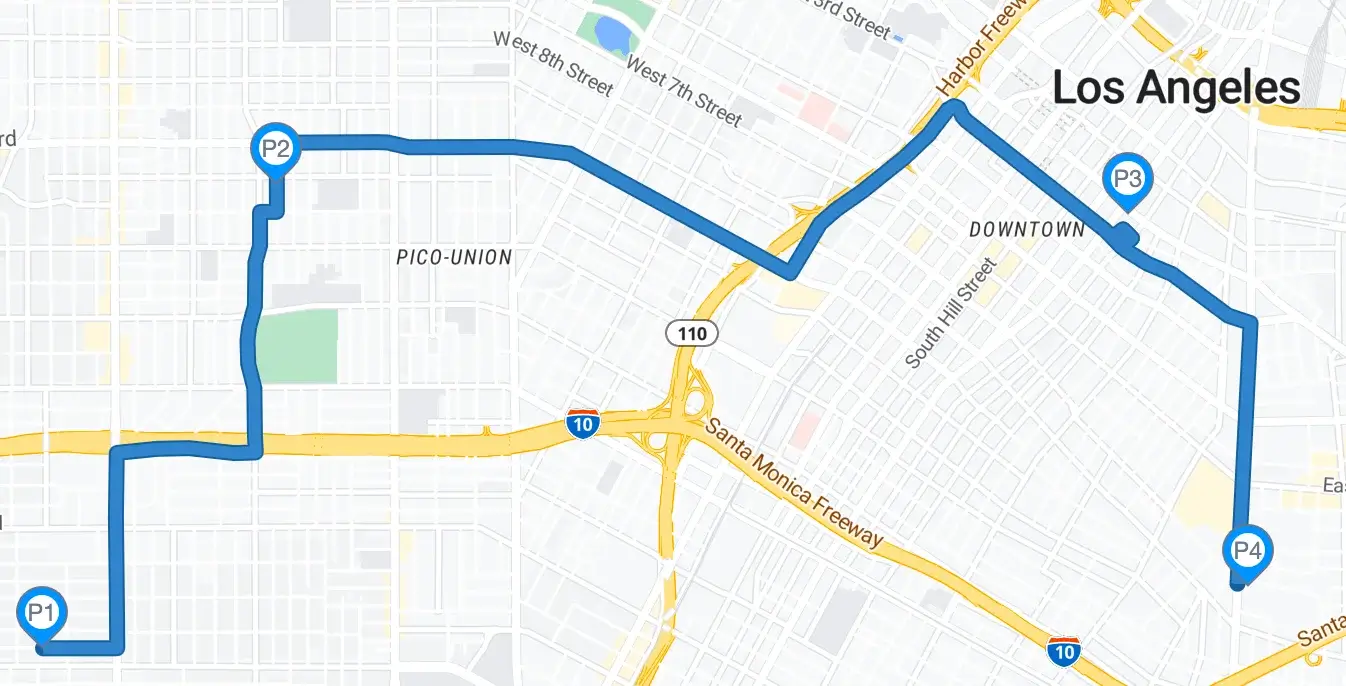
GET Request Example 2
Let’s take a step further and expand the request from Example 1 to add:
-
geometry=geojsonto get the geoJSON details of the snapped path -
get a snapped route that a
truckcan take
Request
Response
Below is a visual representation of the above response. Notice the slight differences in the route that is appropriate for a truck instead of a car from Example 1.
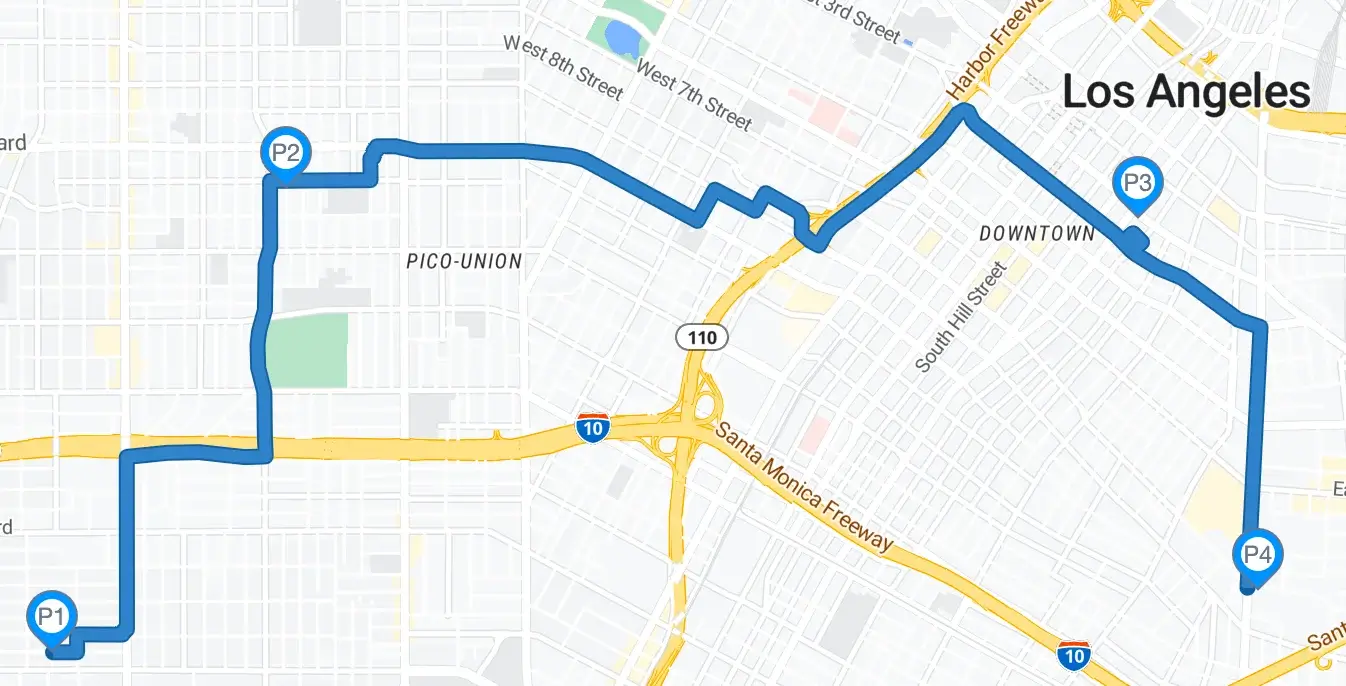
POST Request Example
Now, let’s see how the POST request for the same scenario from Example 2 above looks like
API Query Limits
-
The maximum number of coordinate points that can be added to the
pathparameter in a GET request is 100 and in a POST request is 200. -
NextBillion.ai allows a maximum rate limit of 6000 queries per minute or 100 queries/second for continuous requests. Note: We can increase the quota if needed, on request. Contact support@nextbillion.ai for more details.