Constraints : Maximum Waiting Time
In this example, we learn about the hard constraint of maximum waiting time. NextBillion.ai’s Route Optimization Flexible API provides options to control how long the driver must wait after arriving at the task's location. It is worth noting that this is a hard constraint and applies to all the tasks given in the problem. This feature is helpful when users want to manage the wait times of their drivers or when achieving the lowest wait times is a crucial business goal (for example, consumer-facing services). Let's look at how to incorporate this functionality into an optimization request.
Get Started
Readers would need a valid NextBillion API key to try this example out. If you don’t have one, please contact us to get your API key now!
Setup
Once you have a valid API Key, you can start setting up the components to be used in this example. Let’s take a look at them below.
Jobs & Shipments
We start by defining 5 jobs and 1 shipment. For these tasks we add:
-
A unique identifier for each task
-
Location indexes for each task
-
Specify the schedule of tasks. This is done by adding time windows within which a task must be completed. We have added a 15 min time window for all tasks for the sake of simplicity, but the Route Optimization is capable of handling complex task schedules as well.
-
Skills for each task
-
The actual time taken to complete the tasks once the driver/vehicle is at the task’s location i.e. the service time for each task.
Let’s take a look at the jobs JSON after the above properties are configured:
Vehicles
Next, we add 2 vehicles that are going to fulfill the tasks within the defined constraints. To describe the vehicles and their properties we add:
-
A unique ID for each vehicle
-
Vehicle shift time or the time window
-
Capacity to denote the amount of load that the vehicle can take
-
start_indexto denote the point from where the vehicle would start. Alternatively, the vehicles could also be assigned to adepot. -
costsfor all vehicles. We have specified afixedcost for both vehicles but the readers can useper_houras well.
Once the vehicle and their properties are defined, the resulting vehicles JSON is:
Locations
Next, we define the locations object and add all the locations used in the problem along with a valid id. The locations object with all the points used in this example:
Options
Lastly, we need to enable the max_activity_waiting_time constraint for our problem. We are configuring the constraint to keep the waiting time below 8 minutes for each activity.
Optimization POST Request
Now let’s put all these components together and create the final POST request that we will submit to the optimizer.
Optimization POST Response
Once the request is made, we get a unique ID in the API response:
Optimization GET Request
We take the ID and use the Optimization GET request to retrieve the result. Here is the GET request:
Optimization GET Response
Following is the optimized route plan:
Following is a visual representation of the initial locations of tasks, vehicles and the routes suggested after optimization as per the given constraints.
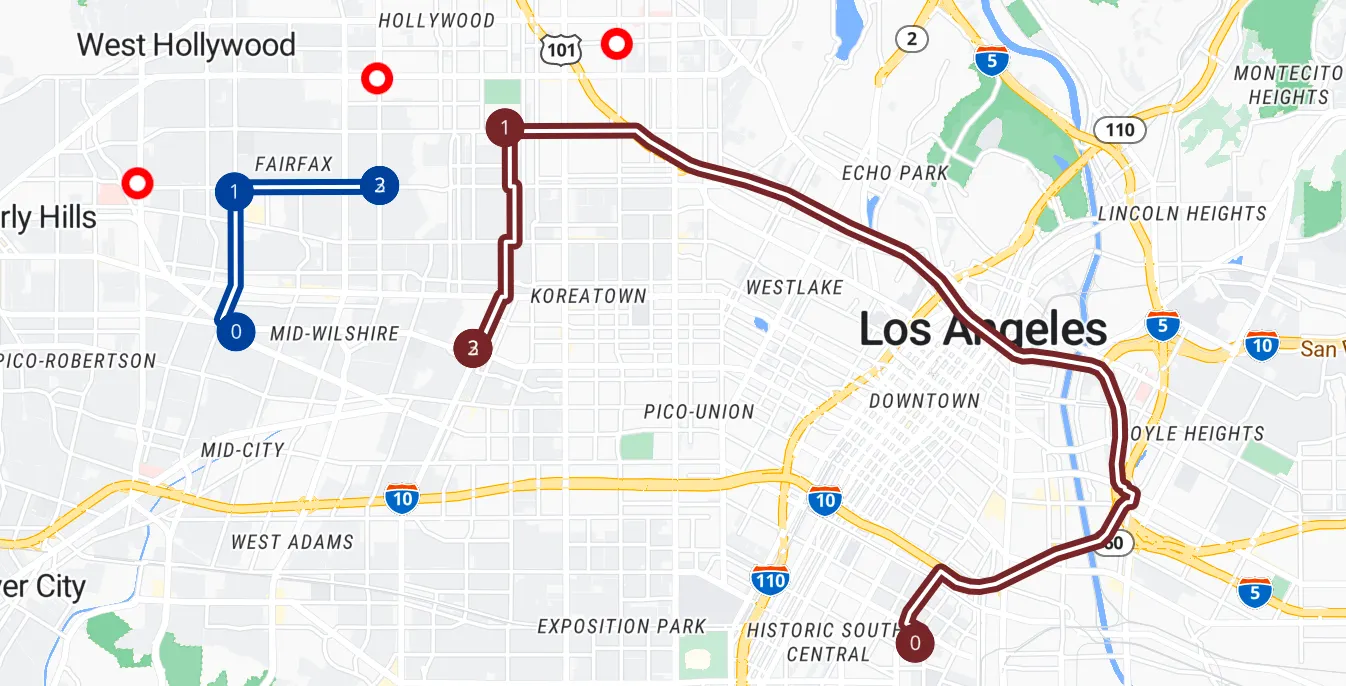
Analyzing the Solution
Looking at the result we can observe some interesting insights:
-
We get an overview of the overall result with a total distance of 24826 meters covered within a total duration of 2276 seconds of driving time to complete all the assigned tasks.
-
Important to highlight here is the total wait time of 718 seconds (~12 minutes) for both vehicles, however 3 tasks remained unassigned as the wait time for them was higher than the prescribed limit of 8 minutes. Please note that readers might see a different number of tasks getting unassigned when trying the example. This would be because of the prevailing traffic conditions at the time of executing the POST request and is totally expected.
-
As evident in the solution, the maximum waiting time strictly adheres to the configured value and that might lead to some tasks remaining unassigned for some cases.
We can experiment with the wait time limit, number of vehicles and time windows etc to explore how job sequencing and assignments change under different scenarios presented to Route Optimization Flexible API.
We hope this example was helpful. Check out some more use cases that Route Optimization Flexible API can handle for you!